evolution of man and mammal

Many traditional family trees show a single lineage, with ancestors producing descendants in one straight line. But the hominid “family tree” is actually more like a bush, with many side lineages that have branched off and gone extinct.

The
Human
Family Tree
All living things, past and present, are connected through evolution. Different hominid species evolved along different—but connected—evolutionary lines. The earliest hominids probably appeared between six and eight million years ago. Our species, Homo sapiens, is young, appearing just 195,000 years ago.


The Quaternary Period
(1.8 million years ago – present)
By the time the Quaternary period began nearly two million years ago, the continents had moved to their current positions, and massive glaciers had formed at the poles. Earth had entered an intense ice age that continues today.
Many mammals evolved to be massive during this period because bigger bodies were better-insulated against the cold climates of the ice age. These mammals spread across the globe as new land bridges connected continents.

Mammoths
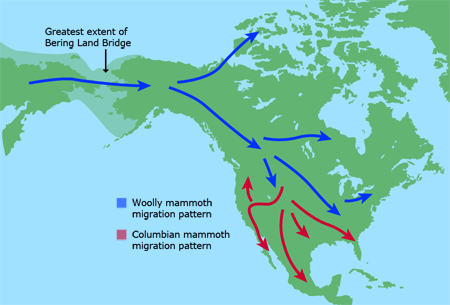
A Mammoth Migration
At least two species of mammoths migrated from Siberia across the the Bering land bridge to North America.
One of the first waves of mammoths occurred about 1.8 million years ago with Columbian Mammoths. These mammoths migrated south and fossils can be found in California, Arizona, Mexico and as far east as Florida.
The more recent wave of Mammoths from Asia occurred about 100,000 years ago. These were the Woolly Mammoths. They lived in northern areas including parts of New England.
Some scientists think mammoths played a part in the arrival of humans in the Americas around 13,000 years ago. As mammoths migrated across the Bering land bridge, humans on the hunt may have followed close behind.


Baby mammoths stayed close to their moms until they were teenagers. The moms protected them from danger and from other animals. If a mammoth’s mom died, one of the other mammoths in the group would adopt the young mammoth.
Like elephants, mammoths were nomadic creatures and traveled in small packs led by females
Despite their size, mammoths were herbivores--their diets consisted only of grass and other plants
One of the defining features of a mammoth is its
inward-curving tusks
Although elephants and mammoths share a common ancestor, elephants did not evolve from mammoths
Mammoths are figured in the cave art of primitive humans

Columbian Mammoths
Columbian mammoths (Mammuthus columbi) inhabited North America as far north as the northern United States and as far south as Costa Rica during the Pleistocene epoch. Reaching 13 ft at the shoulders and 10 tonnes (22,000 lb) in weight, the Columbian mammoth was one of the largest species of mammoth. They also had impressive, spiraled tusks that measured up to 16ft, making them world record holders among the elephant family.
Woolly Mammoths
Woolly mammoths (Mammuthus primigenius) roamed North America, Africa, Europe and Asia 2.4 million years ago during the last ice age. Their thick, shaggy hair and layers of fat helped protect them from the cold temperatures, These mammoths were hunted by early humans and used for food, clothing and shelter. Paleontologists estimate that woolly mammoths could grow to be about the size of the average African male elephant: 9-11 feet tall and weighing as much as 6 tons.

Mammoth Evolution


Mammoth vs Mastodon
Though related and similar in appearance, mastodons and mammoths have some distinct differences. Mastodons ate leaves from trees while mammoths ate grass and mastodons were slightly smaller in stature than mammoths by about 2 meters. Though the two species may have roamed the earth at the same time, mastodons went extinct before mammoths.

Many generations of adults remember coming to the Museum and being transported back to a time when people were living in caves. The first of two Neanderthal family dioramas was installed in 1929, in the Hall of Historical Geology which was located on the Museum's 2nd floor. In 1933, the Hall of Prehistoric Man (located on the Museum's Ground Floor) opened with a series of 8 prehistoric scenes. In the early 1970s, the Neanderthal figures were replaced with new ones made by Museum artist Joseph Krstolich. By 1994, the Hall of the Stone Age of the Old World exhibit had been dismantled because most were considered to be scientifically inaccurate. The Hall had included the Neanderthal Family diorama as well as dioramas depicting Mas d'Azil cave in France (also called Azillian Boar Hunt); Aurignacian Cave Art (Gargas cave, France); Chellean scene in northern France; Neolithic Sun Worship; Solutrean sculptor; Swiss Lake Dwellers; Cap Blanc Rock Shelter and the skeleton of Magdallenian girl.


